In this article we will show you step by step how to set up Google Tag Manager with our new Borlabs Cookie version 3.0 and what you need to be aware of.
If you have previously used Borlabs Cookie 2.0 with the Google Tag Manager, please note the following:
- The event that is fired for consent is now specified by us.
- The GTM can now be integrated locally and is therefore more in line with GDPR principles.
- If you are using the GTM template "Borlabs Cookie Consent Variable" and you get an update suggestion in the GTM, please update it.
The update is also compatible with Borlabs Cookie 2.0, so it can be updated at any time without hesitation.
Configuring and installing Google Tag Manager
Please note: If you are currently working through our quick start guide and using the scanner to install the Google Tag Manager package, you can skip step 1.
Google Tag Manager - Select package
Within Borlabs Cookie, click on Library and search for the Google Tag Manager package.
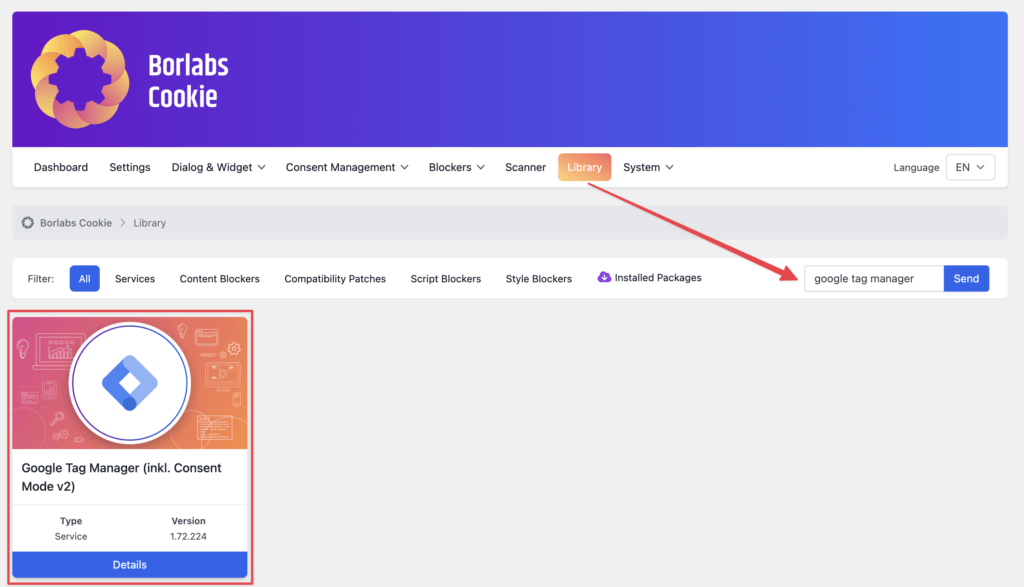
Then click on the Details button here.
Install Google Tag Manager
You will now be taken to the Google Tag Manager package with all the relevant information about Google Tag Manager.
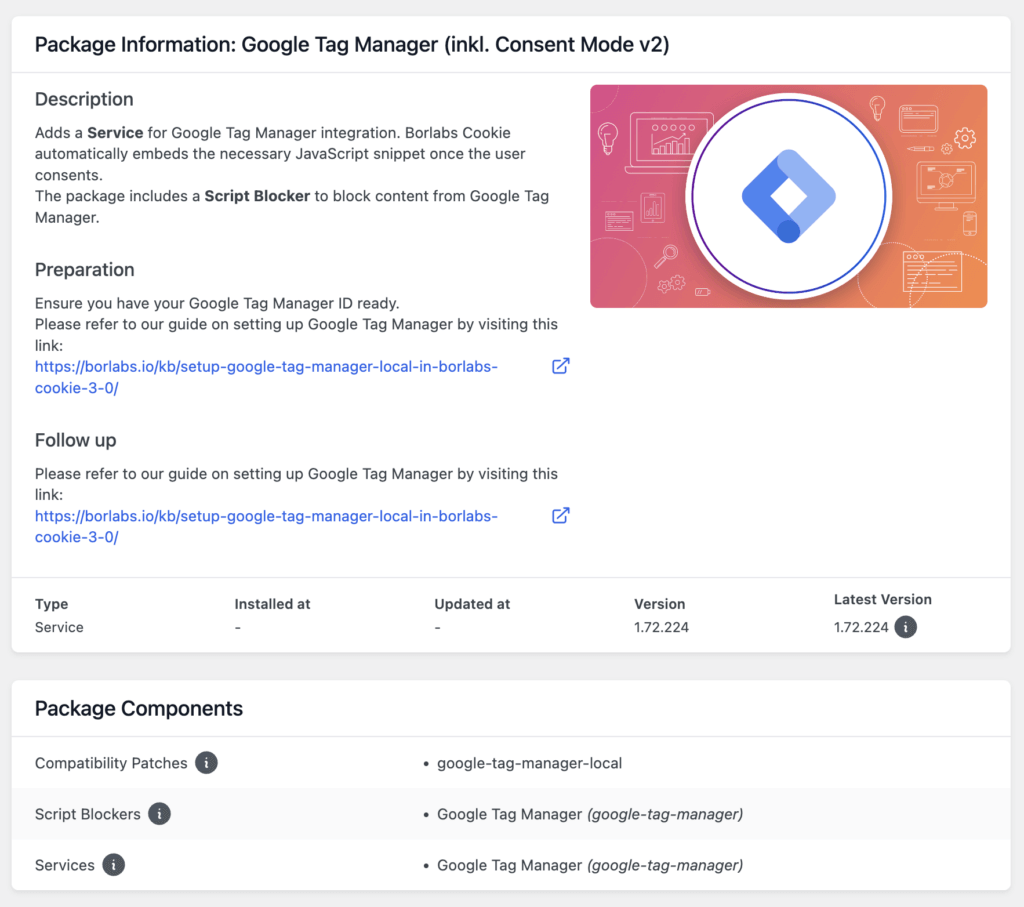
Scroll down to Google Tag Manager - Settings.
Here you enter your GTM ID and can make further settings if necessary.

For all other settings, you will find a corresponding description via the information icon.

Below you will find a very important and new feature of our Google Tag Manager package:
Save the Google Tag Manager locally (our recommendation)
As of our package version 1.39.23, you have the option of caching the Google Tag Manager locally.
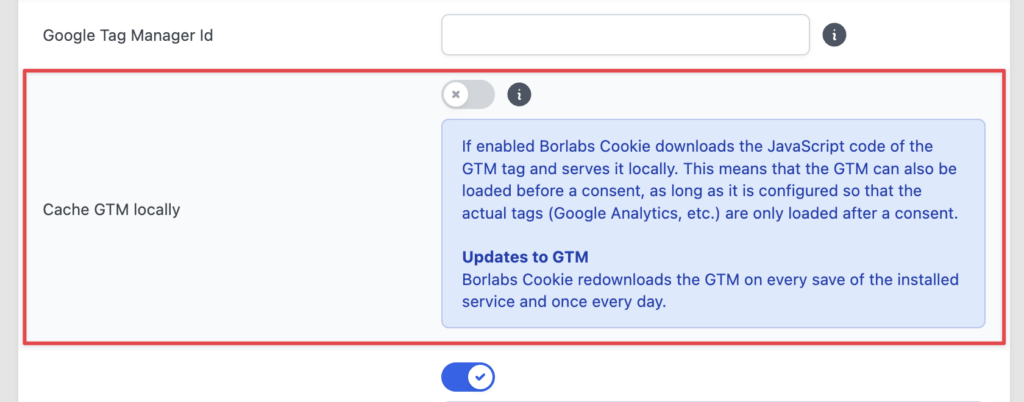
What does this mean for you?
When enabled, Borlabs Cookie downloads the JavaScript code of the GTM tag and serves it locally.
This has the great advantage that the GTM script can also be loaded before consent is given, as long as it is configured in the GTM container so that the actual tags (Google Analytics, etc.) are only loaded after consent is given.
You make changes in the GTM container on Google:
If you use the GTM with this function (locally) and make changes directly in your GTM container on Google, these changes will not be directly enabled in the Borlabs cookie.
IMPORTANT: In order to make sure that the published changes in your GTM container are also adopted by Borlabs Cookie, you need to go to the Google Tag Manager service and click on the "Save settings" button.
You are using the Google Tag Assistant (View in preview):
When you use Google Tag Assistant to test your setup, the default code (non-local) is always loaded without exception. This means that changes in the GTM will take effect immediately.
Once you have entered all the necessary details and completed your configuration, click on the Install button.
Consent Mode
As Consent Mode is recommended by Google, you can enable it during the Google Tag Manager setup process using the Activate Consent Mode feature.
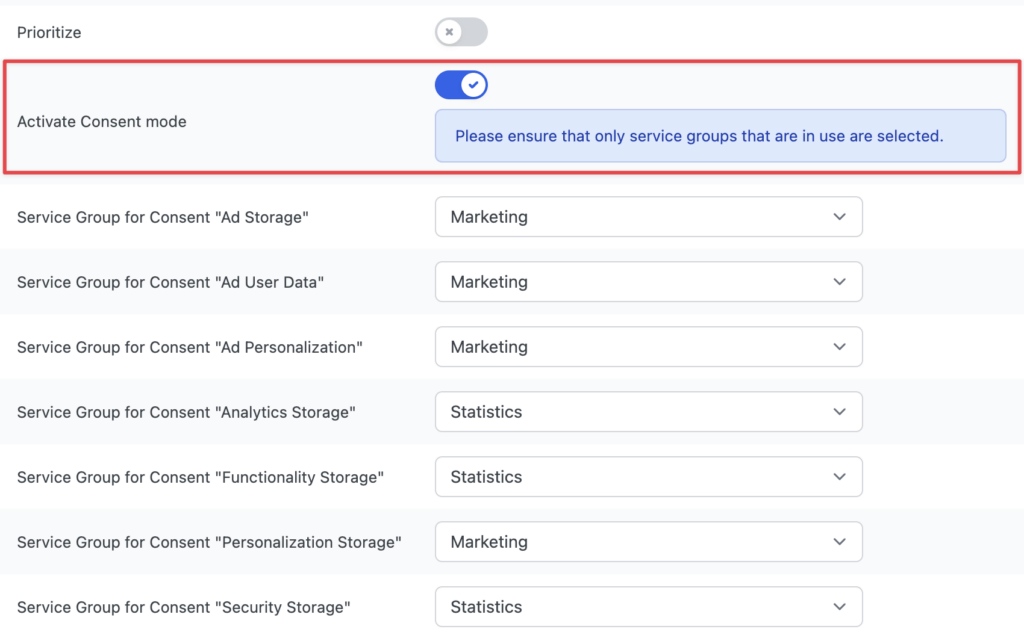
You will then have the option of selecting which Service Groups should be assigned to which Consent Type.
This is necessary because Consent Mode consents are not based on individual services, such as Google Analytics, but on general data processing.
In the configuration shown in the screenshot, for example, consent for the "Marketing" Service Group would result in consent for "Ad Storage", "Ad User Data", "Ad Personalisation" and "Personalisation Storage" being sent to Google.
For example, if the Marketing Service Group is selected, at least one active service must be assigned to the Service Group.
The new consent mode offers the following pre-defined consent types:
| Ad Storage | Enables the storage of advertising-related data such as cookies |
| Ad User Data | Defines the consent to send advertising-related user data to Google |
| Ad Personalization | Sets the consent for personalized ads |
| Analytics Storage | Enables the storage of analysis-related data such as cookies, e.g. on visit duration |
| Functionality Storage | Allows storage of data that supports the functionality of the website or application, e.g., language settings. |
| Personalization Storage | Enables the storage of data related to personalization, e.g. video recommendations |
| Security Storage | Allows storage of security-related data, e.g. for authentication, fraud prevention and other user-protecting mechanisms |
If cookie-less tracking is used, the 2.3.1: Add trigger in GTM section should use the Page view trigger and the 2.3.2. Optional: Add additional triggers section must be skipped.
This only applies to tags that natively support Advanced Consent Mode. All others must be triggered and blocked as described in the guide if they are not essential and require consent.
This procedure is legally controversial. To be on the safe side, follow the guide as described.
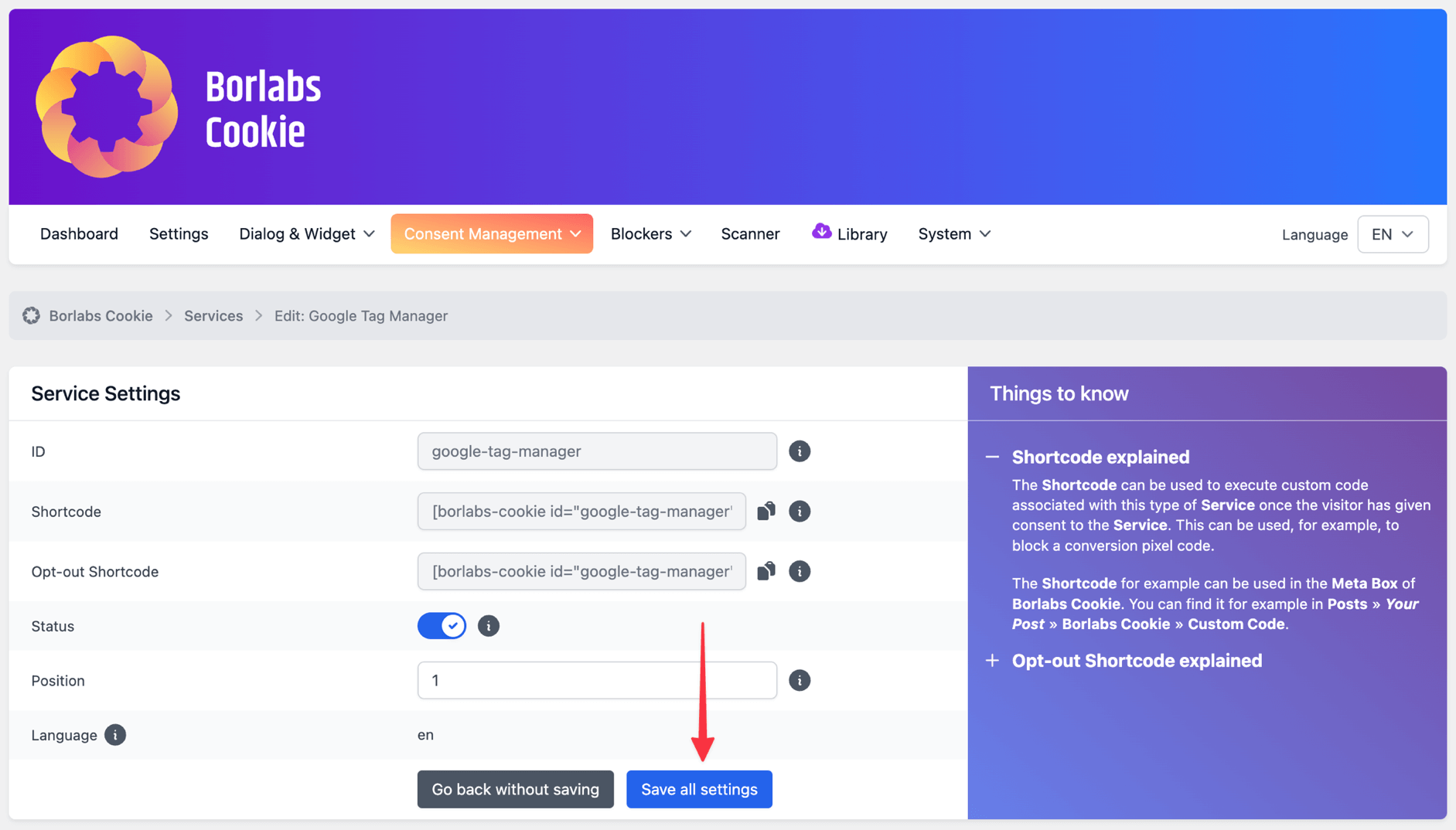
The Google Tag Manager package is now installed and all necessary settings and data are set up and stored in Borlabs Cookie.
If you now go to Services, where you can see all the Services that have been set, you will also find the previously installed Google Tag Manager.
Add service
Our example shows how to set up Google Analytics with Google Tag Manager in Borlabs Cookie.
You can set up any service with the Google Tag Manager. To do this, simply proceed as described in these instructions - in this case Google Analytics.
Go to the library and search for the Google Analytics package - if not already installed!

Then click on Details.
This will take you to the Google Analytics package information. Enter your tracking ID and click the Install button.

Prepare the service for the GTM
Once you have installed the package, open the settings for the service. To do this, click on Consent Management → Services.

Once you are in the settings, scroll down to Additional settings.
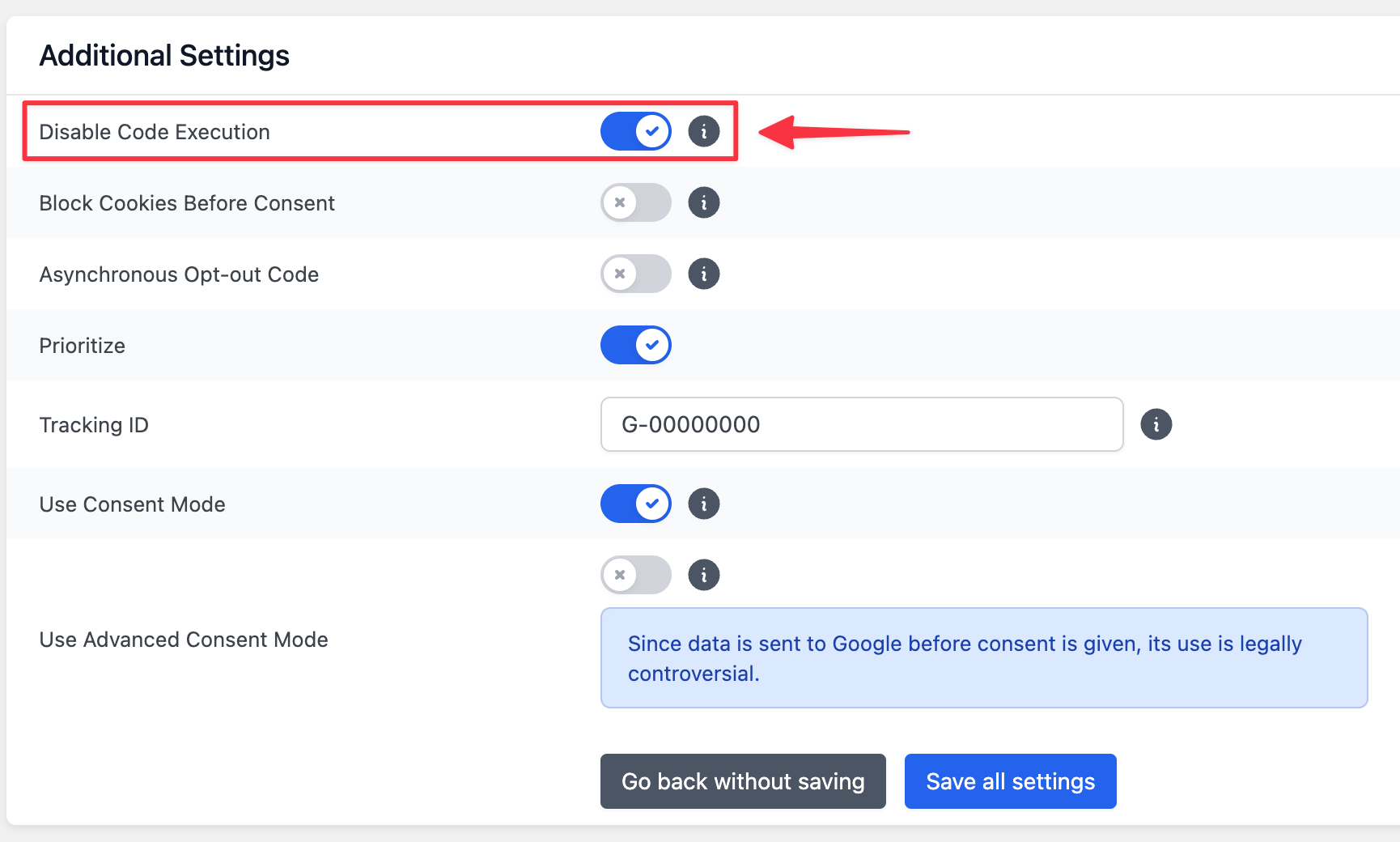
Difference between Basic Consent Mode and Advanced Consent Mode
When setting up the service in Google Tag Manager, there are two options: the basic consent mode and the advanced consent mode. In basic consent mode, the tag is only delivered if consent has already been given for the corresponding service via Borlabs Cookie.
This is the safest option from a legal point of view and works for all tags!
In the advanced consent mode the tag is also delivered without consent.
However, the tag automatically recognizes that consent has not yet been given and therefore only sends a small amount of data. This sending of less data is called a ping by Google.
Differences summarized:
Basic Consent Mode
- Legally more secure
- Works for all tags
Advanced Consent Mode
- Only works with supported tags (e.g. Google Analytics and Google Ads)
- Unclear from a legal point of view
- Collects cookieless pings from users who have not given consent > More data
- Easy setup in under 5 minutes, see 2.4. b) Advanced Consent Mode
Currently, Google tags such as Google Analytics or Google Ads support the advanced consent mode.
If you want to use advanced consent mode for a tag that you are not sure supports it, you can check in the tag in GTM under Advanced Settings > User Consent Settings > Built-in Consent Checks to see if there are any consents that are supported.
If consents are listed there, it is very likely that the advanced consent mode is supported by the tag.
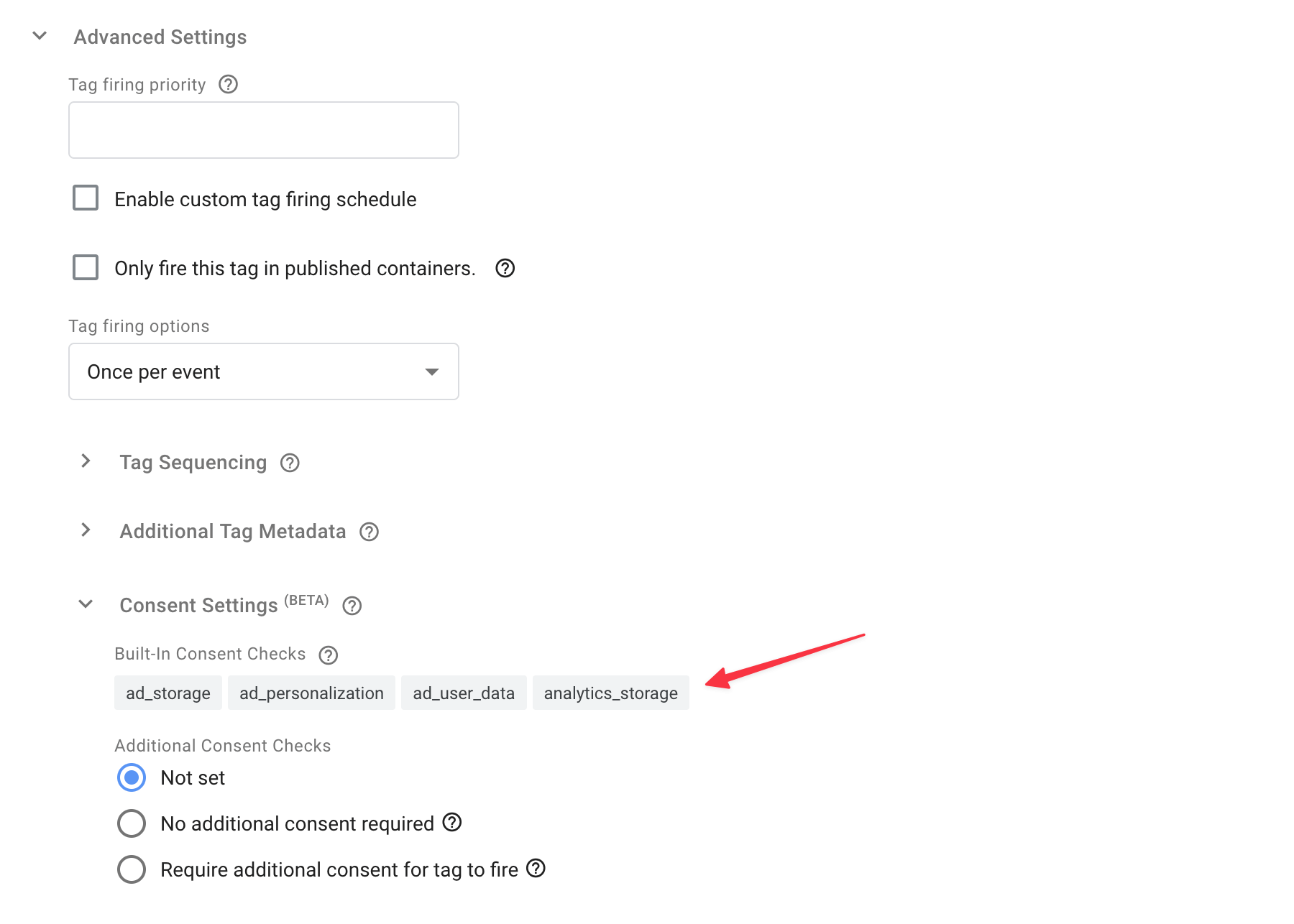
a) Basic Consent Mode
Now go to your Google Tag Manager container and create an event/tag and a trigger for Google Analytics.
To do this, click Tags and then New.
Select the Google Analytics tag type here.

Now select the corresponding events/tags.
Enter your Google Tag ID or Google Analytics ID in the appropriate field and save.
Add a trigger in the GTM
Click on Trigger configuration to add a trigger.
Select the Custom event here.
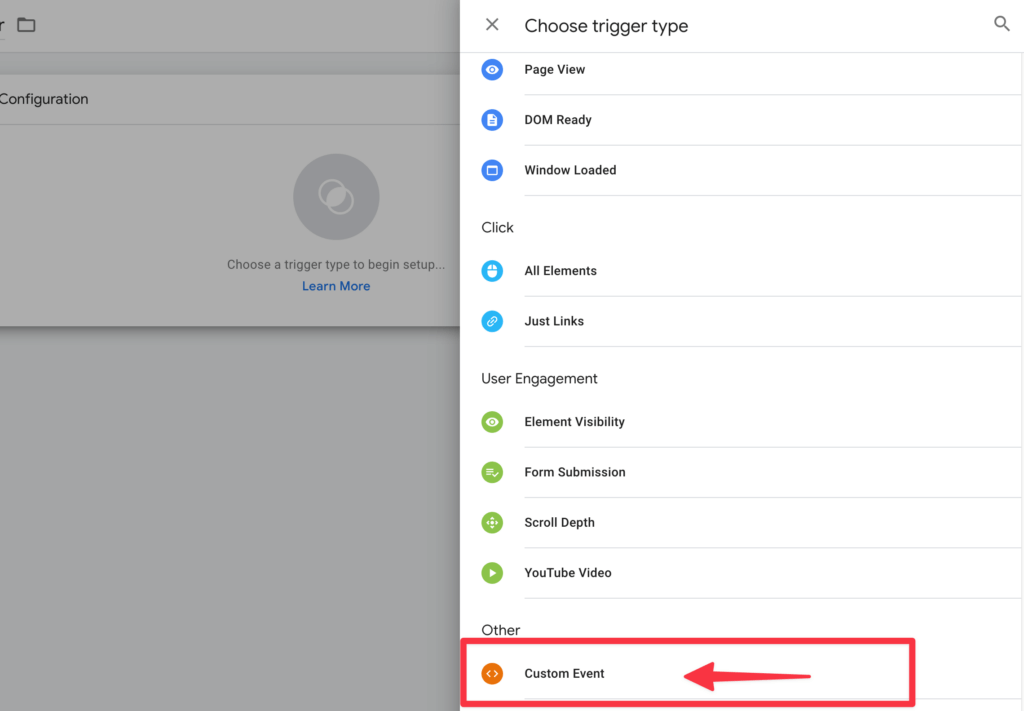
Then enter the event we provide in the appropriate field.
The Google Tag Manager package ensures that a corresponding GTM event is automatically sent for each service - with the name borlabs-cookie-opt-in- + ID of the service.
For example:
Google Analytics: borlabs-cookie-opt-in-google-analytics
Meta-Pixel: borlabs-cookie-opt-in-meta-pixel
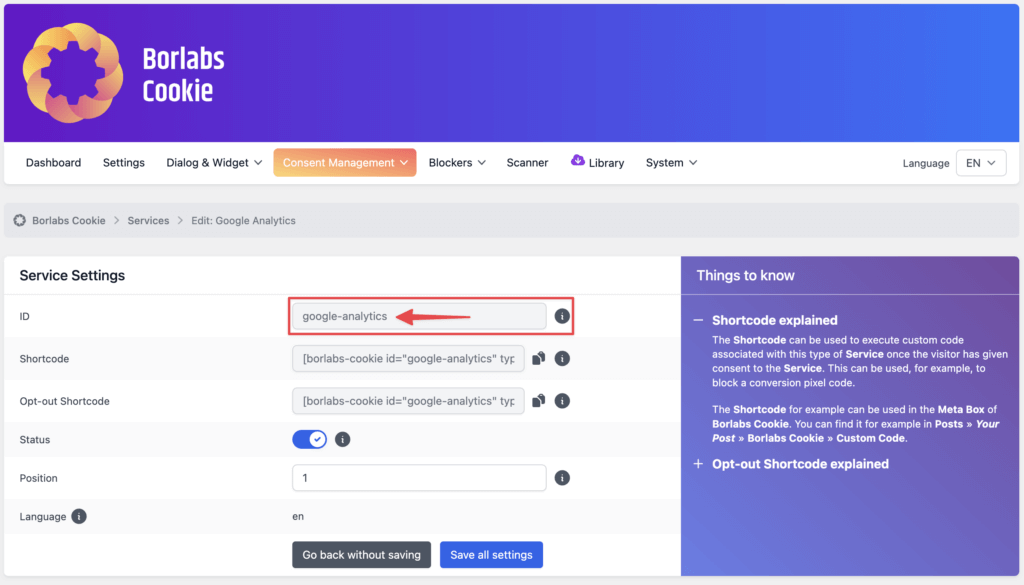
In our case, the service has the ID google-analytics.
Therefore, when consent is given, the event borlabs-cookie-opt-in-google-analytics is sent.
Our integration ensures that the event is executed no more than once per page view. It is therefore not necessary to create a trigger group for the page view.
The event can also be used as an alternative to the page view trigger for the tag.
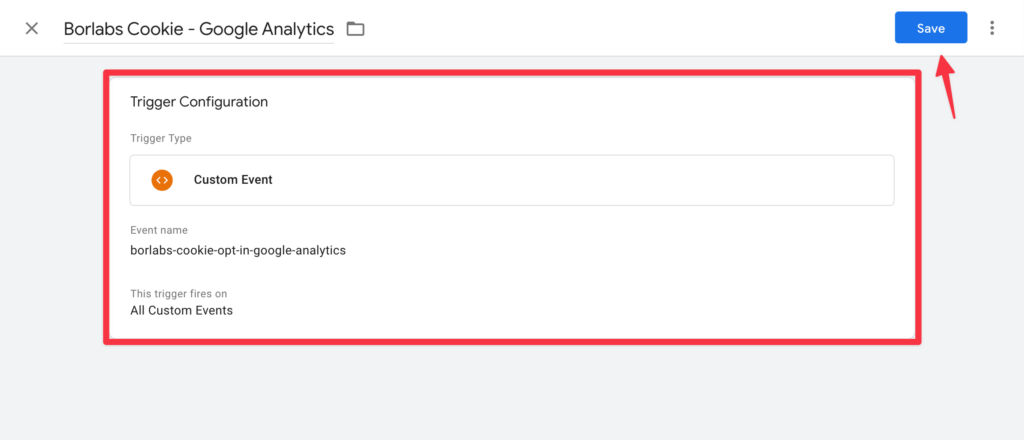
Then click on the Save button.
The setup between Borlabs Cookie and the Google Tag Manager is now complete.
Optional: Add additional triggers
Below is an example of how to add additional triggers. The same instructions can be used for other triggers.
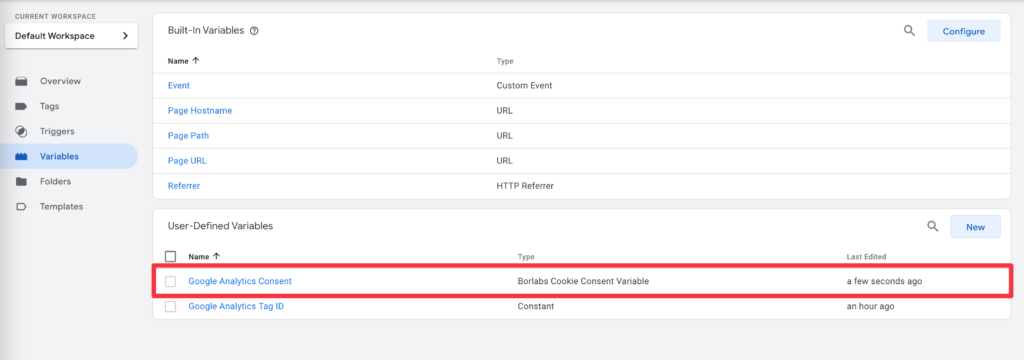
Please note: For all trigger types, the condition Google Analytics Consent | is equal to | true must be added and the Google Analytics Consent variable must have been created once beforehand.
The one-time creation of the consent variable is explained in "Creating a variable for blocking".
Add variable template
In order to block a trigger on a consent, we need a variable for the state of the consent.
To make creating this variable as easy as possible, we have published a template in the Google Tag Manager Template Gallery.
This template must be imported before it can be used.
If you have already imported the template for a Borlabs Cookie 2 installation and are prompted in GTM to update, please do so.
To do this, go to Templates and click on Search in gallery.

Select the template Borlabs Cookie Consent Variable.
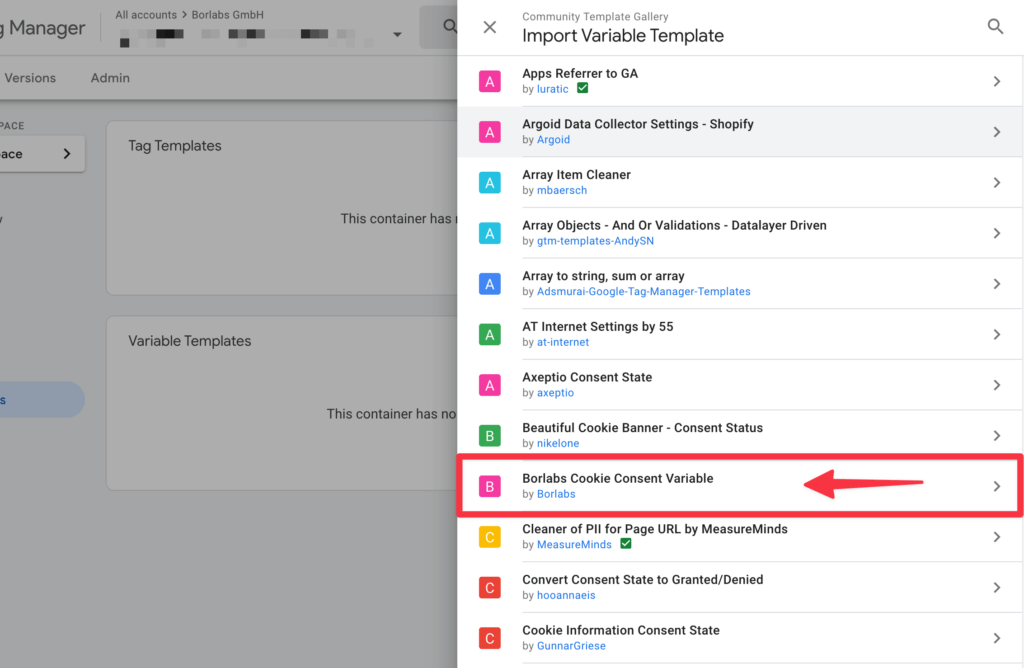
Click on Add to workspace in the top right hand corner.

The Google Tag Manager will now ask you again for the necessary permissions.
Click on Add here.
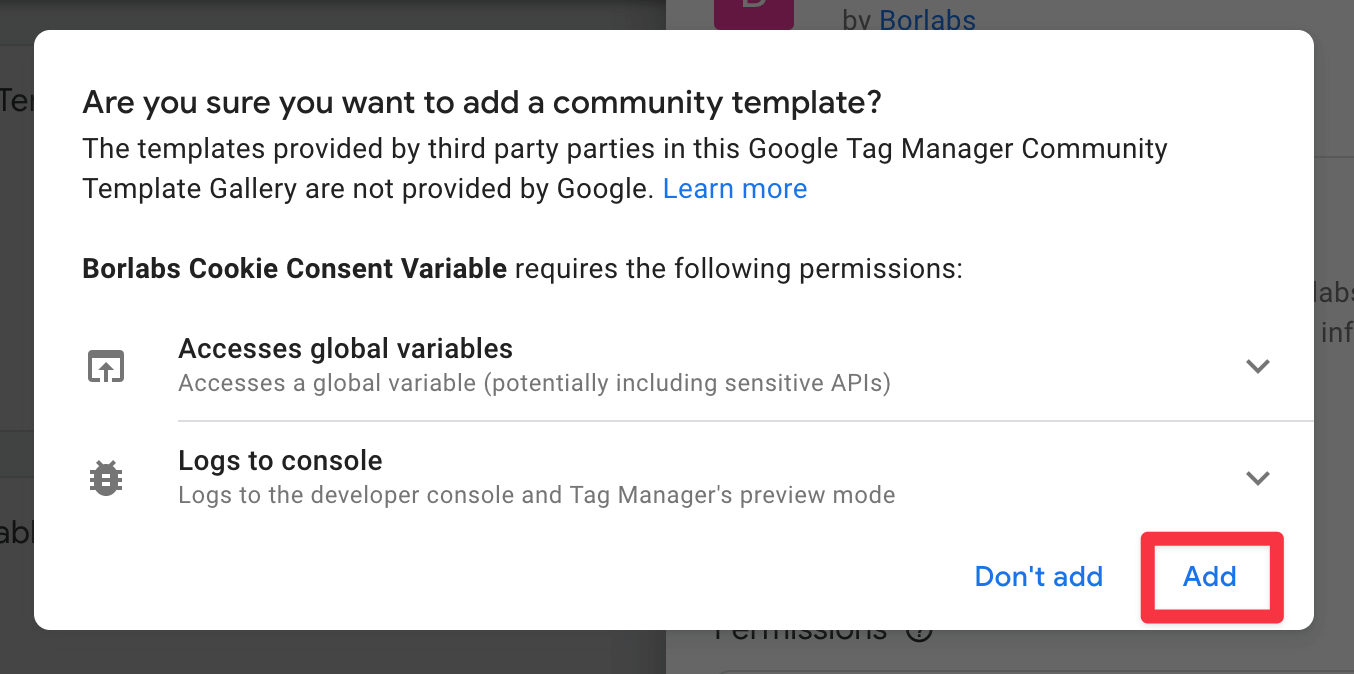
The template should now be added.
Create variable for blocking
In order to ensure that the trigger is only activated when consent for Google Analytics has been given, we need to create a custom variable. To do this in Google Tag Manager, navigate to Variables in the left hand menu and click on New under Custom Variables.
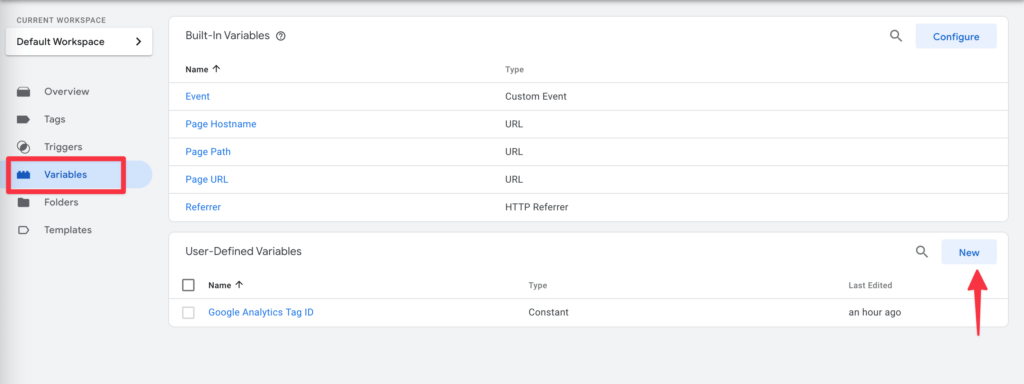
Select the Borlabs Cookie Consent Variable template.
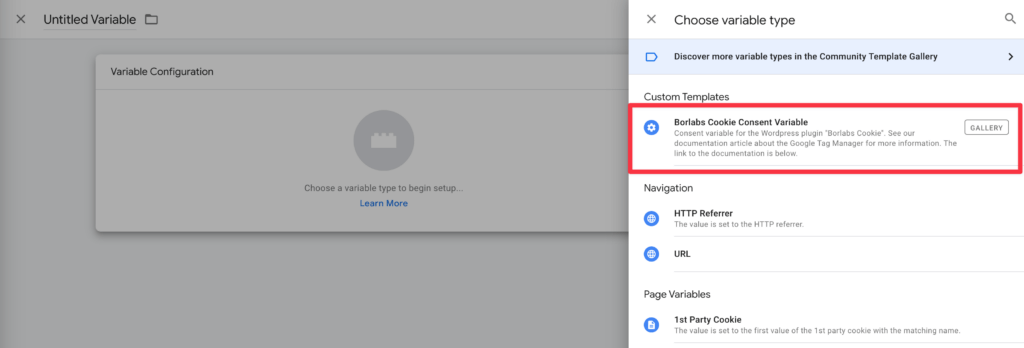
Now you need to enter the ID of the service in the Borlabs Cookie Plugin in the Key of the service/cookie field.
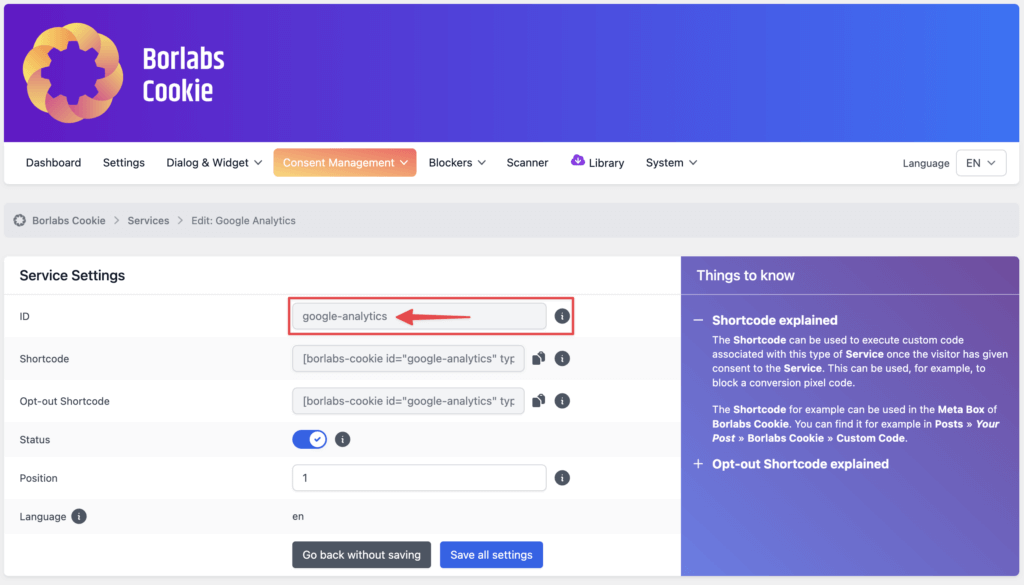
In our example, this would be the ID google-analytics.

If you are not sure what exactly to put into this field, you can look up and copy the ID in the cookie settings in the Borlabs Cookie plugin.
Now give the variable a meaningful name in the header of the Create Variable section, such as Google Analytics Consent, and then save.
Example 1: Creating a tag to track clicks on specific links as an event
As an example, we will create a trigger that sends a specific CSS class as an event to Google Analytics when a link is clicked.
To do this, we give the link a CSS class in WordPress. In this example, the class is sales-link.
First we need to create a trigger for this.
To do this, go to Trigger in the left-hand navigation of the Google Tag Manager and click on New.
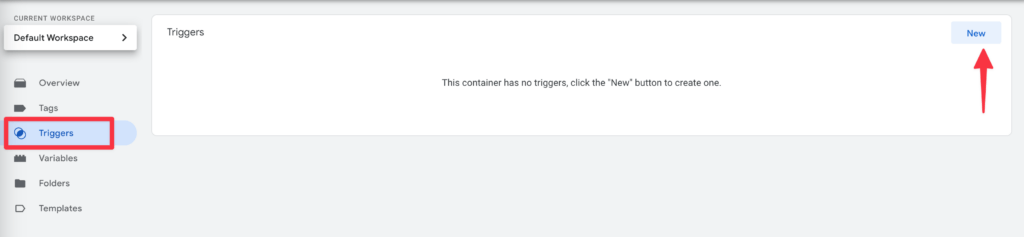
Click on the Trigger Configuration area and select Left only under "Select trigger type".
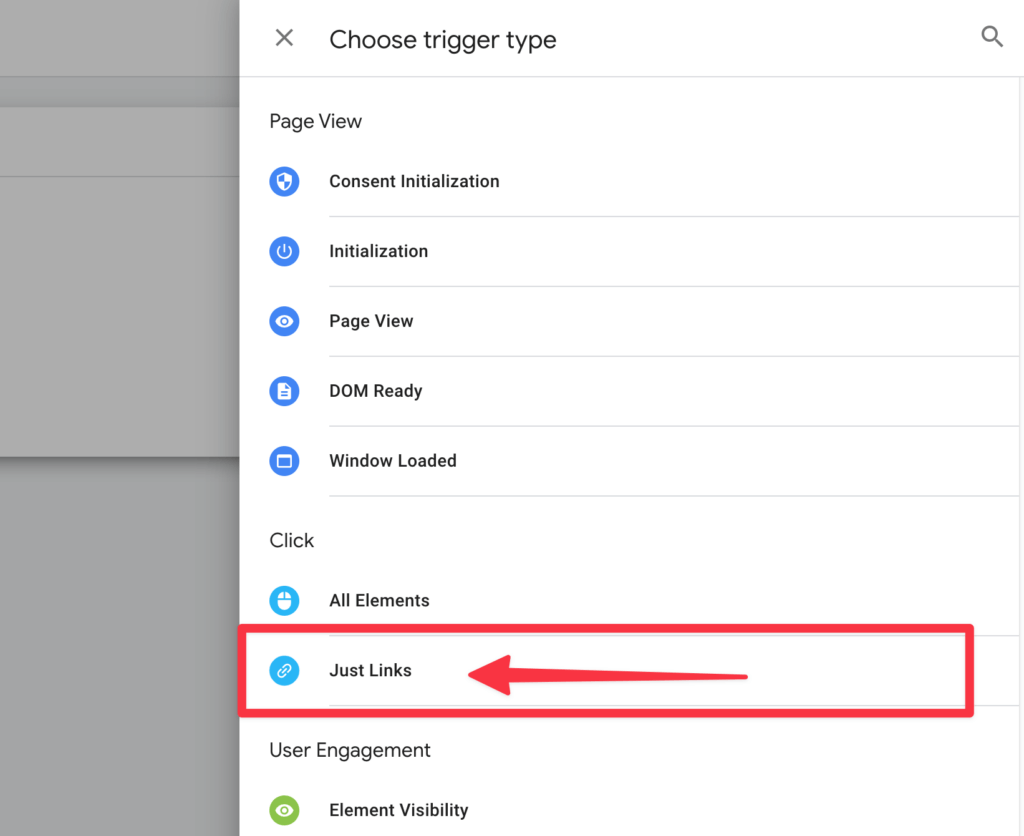
Now select Some clicks on links and add the following conditions:
- Click Classes | contains | sales-link
- Google Analytics Consent | is equal to | true
If Click Classes is not in the list, select Select integrated variable and then select Click Classes.
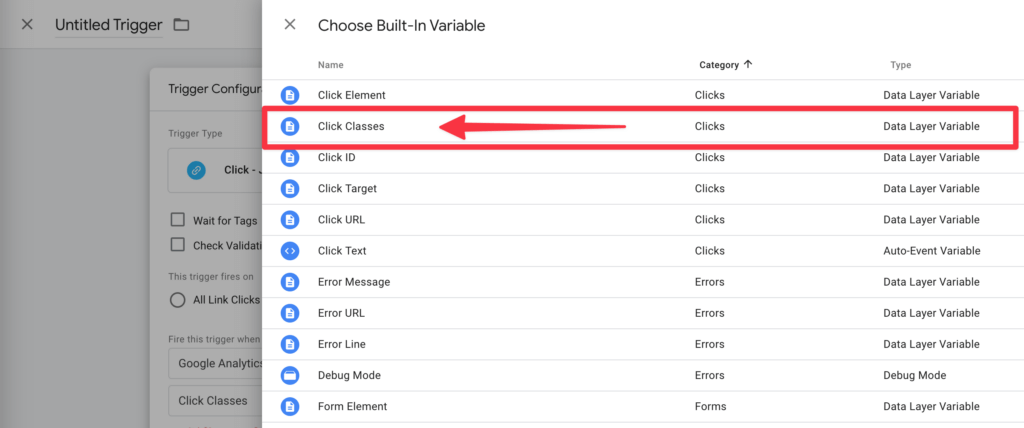
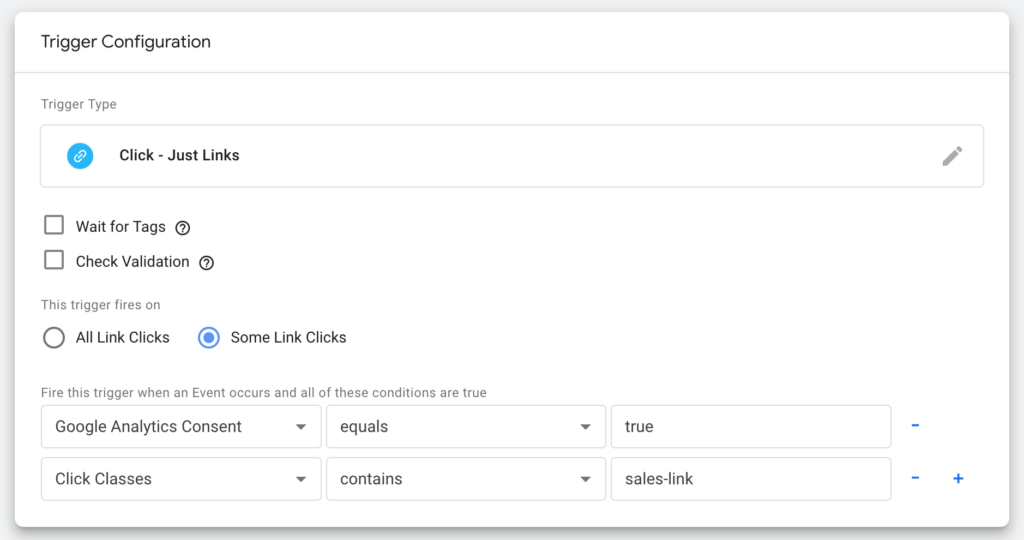
We then name the trigger Click - Sales Link and press Save.

Finally, we need to create a tag for the Google Analytics event.
To do this, go to Tags in the left-hand navigation of the Google Tag Manager and click on New.
Click on the Tag configuration section and select Google Analytics under Select tag type.
Now select the Google Analytics: GA4-Event tag under Tag Configuration.
For this example, we will use the event name sales-link-clicked (which is freely selectable).
To link the tag to the trigger you have just created, click on the Trigger section and select the Click - Sales Link trigger under Select Trigger.

Then save the tag with a name of your choice (in our case Google Analytics Sales Link Event).
Example 2: Enhanced Ecommerce tracking using the Google Tag Manager Plugin
Follow the instructions in this guide to configure the Google Tag Manager for Enhanced Ecommerce Tracking: https://gtm4wp.com/google-tag-manager-for-woocommerce/how-to-setup-enhanced-ecommerce-tracking-google-analytics-4-ga4-version.
When creating a trigger, please note that the condition Google Analytics Consent | is equal to | true must be added.
Here is an example from the guide:
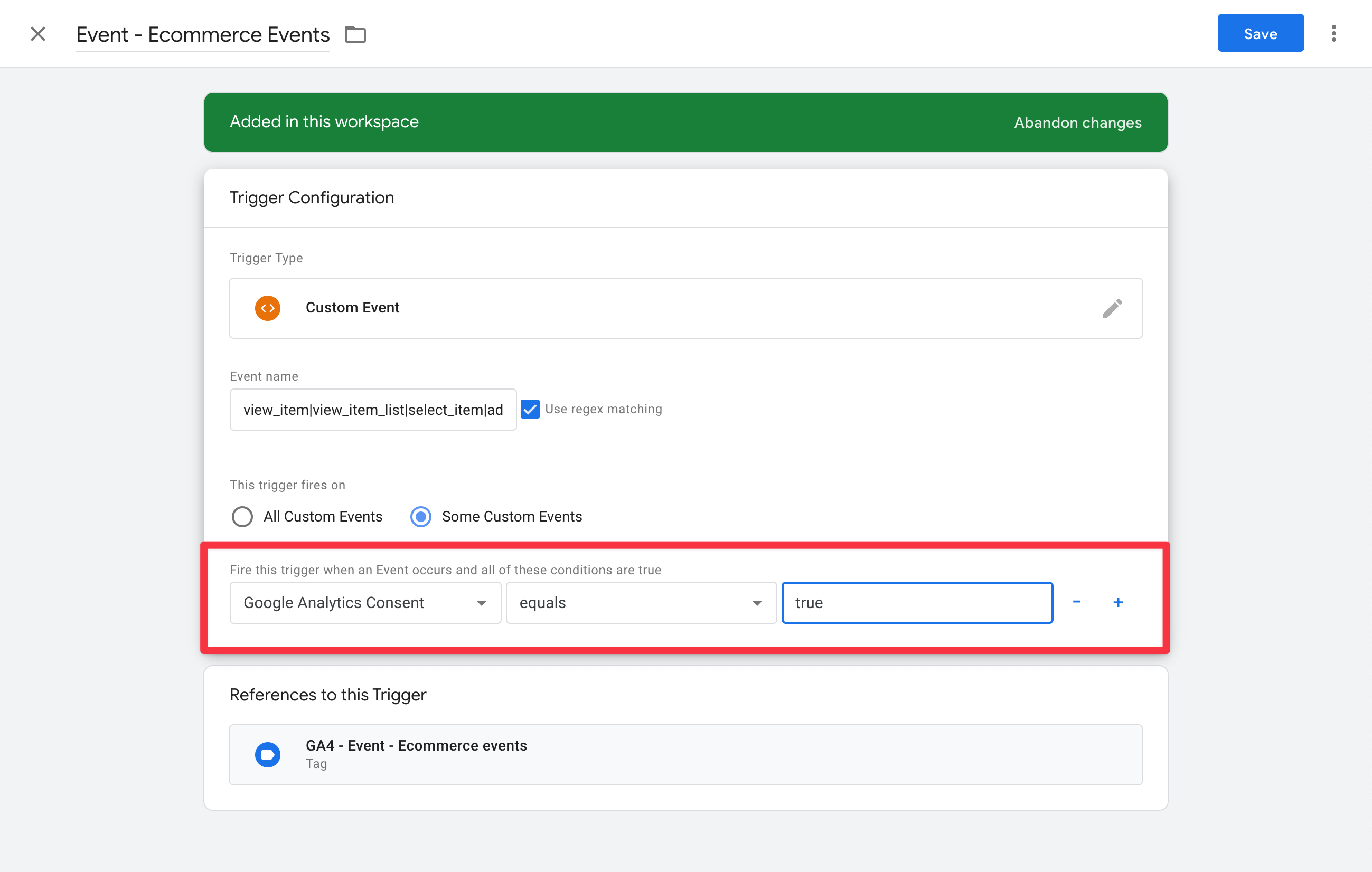
Finally, you need to save your changes. To do this, press the Send button in the top right-hand corner of the navigation bar.
This is because the tags with the consent mode recognize that consent has not yet been given for things like Analytics Storage. Until consent is given, data is only sent to Google Analytics in an anonymized form and no cookie is set.
b) Advanced Consent Mode
In Advanced Consent Mode, the tag can be triggered as usual with the Page View trigger.
Additional triggers, such as when a button is clicked and an event is sent to Google Analytics, do not need to be manually blocked. This also applies when using the "Enhanced Ecommerce Tracking" of the "GTM4WP – A Google Tag Manager (GTM) plugin for WordPress by Thomas Geiger".
Testing with Google Tag Assistant
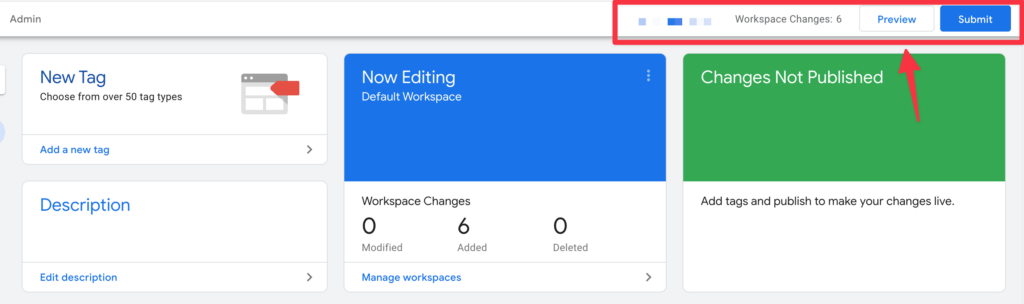
When you want to make sure your setup is working, you can use Google Tag Manager to test your trigger and tag execution.
To do this, click Preview in Google Tag Manager at the top of the page
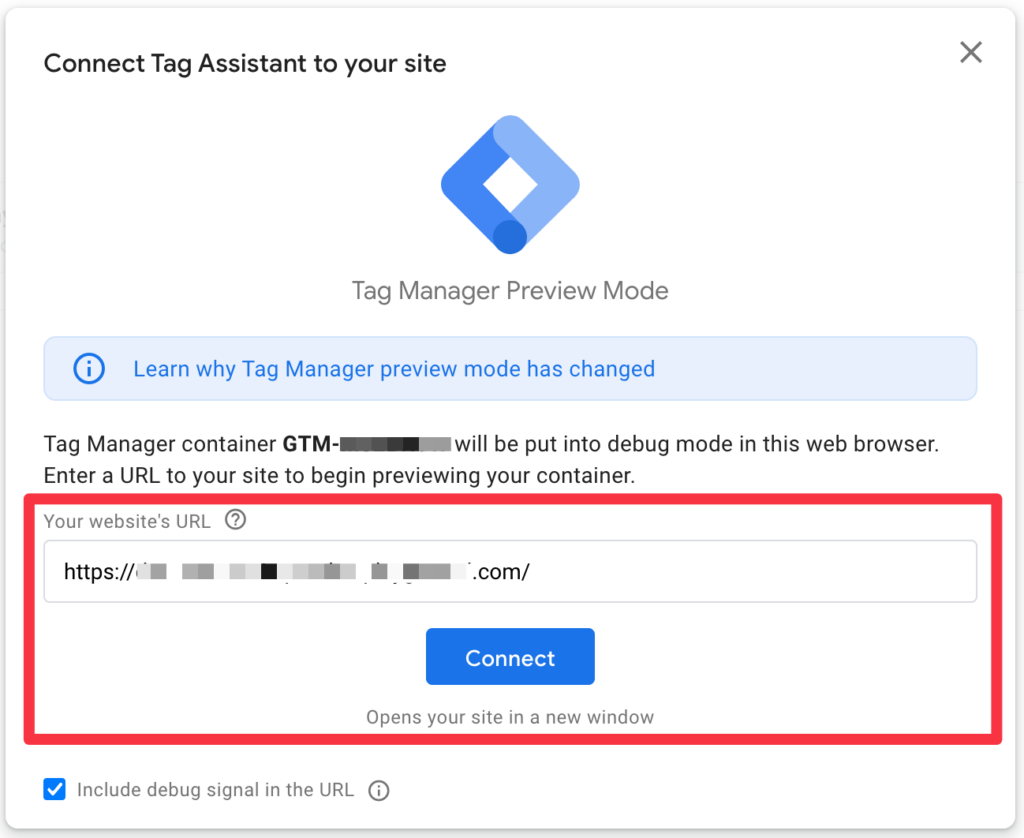
Now enter your URL in the corresponding field and click on the Connect button.
When Consent Mode is enabled, all consents are set to Denied by default until the container is loaded.
Image 1 (Consent Mode "Denied"):
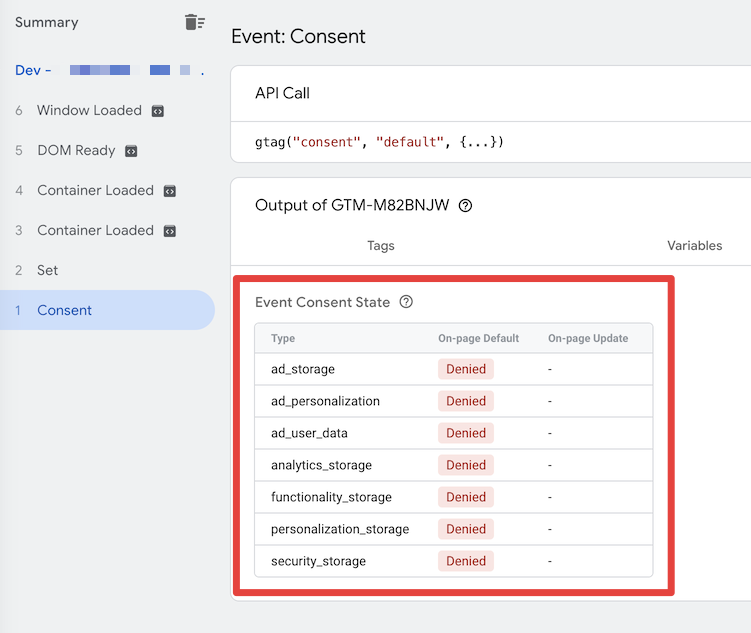
If a consent has been given via Borlabs Cookie, the consents are set to Granted depending on the setting. In the following example, all service groups have been accepted.
Image 2 (Consent Mode "Granted")
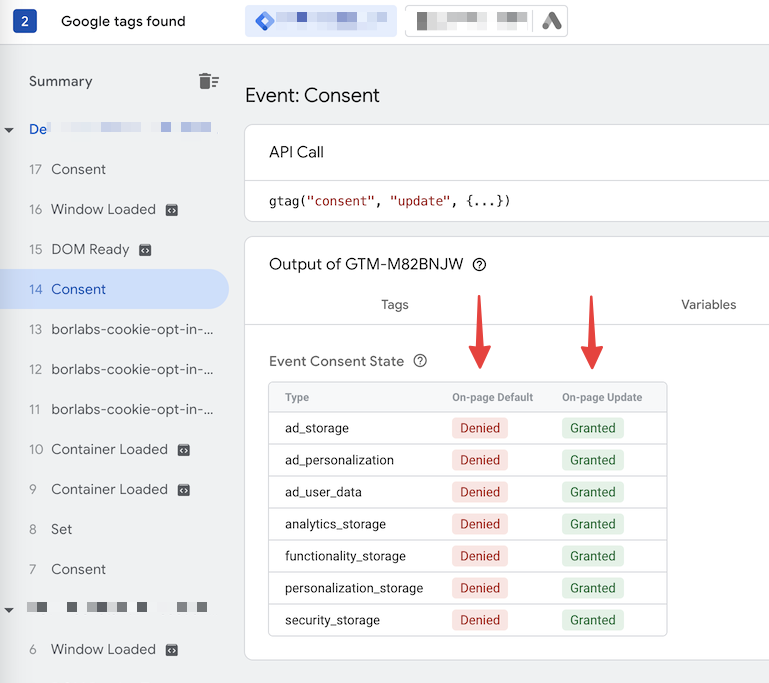
Regardless of the consent mode, Borlabs Cookie's Custom Events can also be viewed in the Tag Assistant.
There is one Custom Event per service that is only pushed when the service is accepted.

Once everything is set up correctly, save your settings and publish your Google Tag Manager container by clicking the Submit button.